Start your project
You must use our design templates to create your design.
After downloading the templates, open inkscape the format you prefer, as if it were a normal file, then start drawing.
For Inkscape 0.92 and higher, by opening the template file, you must select these options:
- Contains graphics for physical devices, such as paper or 3D printers.
- The accuracy of the dimensions and positions of the objects is a priority
Make sure you draw within the template and that the orange box matches the dimensions shown.
You can design for laser cutting in one of five different material formats:

P1
useful size:
181 x 181 mm

P2
useful size:
384 x 384 mm

P3
useful size:
790 x 384 mm

P4
useful size:
790 x 790 mm

80×45
useful size:
800 x 450 mm
available only for
felt and cardboard
How to draw for the laser
The color used for the drawn lines determines what the laser will do, whether it is a cut or an engraving.
For example, if you draw a bird with a blue outline, the laser will cut a bird ...

If you convert the same lines in red, the laser will engrave the bird on the chosen material, and so on.
It's that easy!
Now let's get to the details ...
Cutting lines
The basic part of your design are the shapes you will cut.
The simplest way to visualize how this will turn into your project is to imagine placing on a sheet of paper the pieces you would like to make, and then draw their outline on the sheet with a pencil. Your file should remember that sheet with the lines drawn.
To obtain a cutting line, draw a line or shape.
Then open the window Object> Fill and Stroke and set 'Stroke style' to a thickness of 0.010 mm:

Then set the color of the track from 'Stroke paint', as blue with the RGBA values of 0, 0, 255, 255:

Engraving of vector lines
The vector etching process is very similar to the cutting method, but instead of piercing the material, the laser only affects the surface.
The laser will move along the engraving lines in your drawing. There are three different levels of engraving available: light, medium and deep, each with a different intensity and therefore depth. All three incisions are drawn very precisely with subtle lines, roughly the same size as the laser beam.
Trace thickness
Open the window Object> Fill and Stroke and set 'Stroke style' to a thickness of 0.010 mm:

Light vector engraving
Open the window Object> Fill and Stroke and sets the color of the trace from 'Stroke paint' as magenta with the RGBA values of 255, 0, 255, 255:
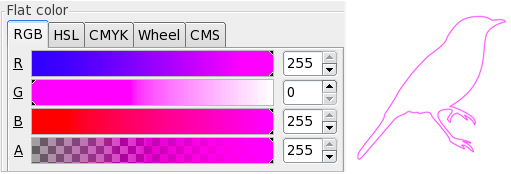
Vector media engraving
Open the window Object> Fill and Stroke and sets the color of the track from 'Stroke paint' to green with the RGBA values of 0, 255, 0, 255:
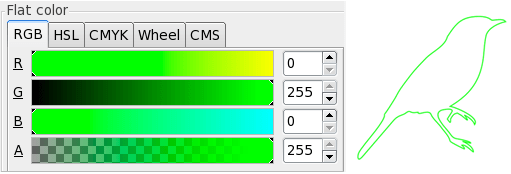
Deep vector engraving
Open the window Object> Fill and Stroke and sets the color of the track from 'Stroke paint' to red with the RGBA values of of 255, 0, 0, 255:

Engraving of raster fills
Generally, raster fills are used for areas with backgrounds, but you can also make a raster engraving of lines that have a track with a thickness greater than 0.3mm. Engraving in raster mode a thinner line will probably not lead to good results.
The scale of the raster engraving goes from the black that corresponds to the most marked incision, up to the very light gray that will make the engraving lighter (or white, which corresponds to the null incision). You can use any grayscale between the two extremes, but remember that the three RGB values must be equivalent. Make sure you use solid and spot colors and no patterns or textures.
To obtain a more defined border in an area engraved with a raster pattern, combine the black or gray fill with a track corresponding to a vector engraving.
The values of the engraving depth are indicated in the "technical details" tab of each material in the catalog.
The incisions do not change according to the thickness of the material (unless otherwise indicated in the sheet).
Engraving of light raster fills
Open the window Object> Fill and Stroke and sets the fill color from 'Fill' to light gray with the RGBA values of 230, 230, 230, 255:

The light raster engraving is absolutely superficial, altering the color of the material without going deep.
Engraving of medium raster fills
Open the window Object> Fill and Stroke and sets the fill color from 'Fill' to gray with RGBA values of 128, 128, 128, 255:
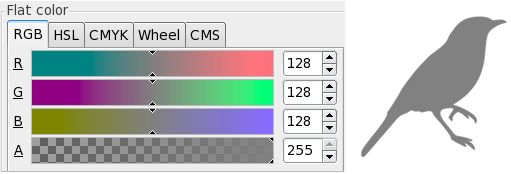
Engraving of deep raster fills
Open the window Object> Fill and Stroke and sets the fill color from 'Fill' to black with RGBA values of 0, 0, 0, 255:

To use the text
All the texts inserted in your drawing must be converted into tracks (paths). In this way the laser will follow your drawing correctly, even without having the same installed font.
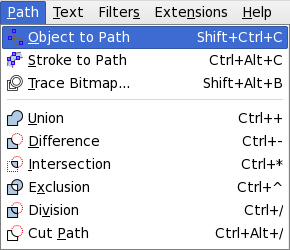
To turn the text into tracks, just select it and then choose Path> Object to Path from the top menu. Once you run this command, you will not be able to edit the text, so do this after checking the spelling!
You can create texts using fills for raster engravings, lines for vector engravings, or a combination of the two types of incisions.
To use images
Our making system takes into account only the drawings in vector, Ignore all the images inserted in other formats (like.jpg or .bmp).
If you want to insert a non-vector image in your file, you have to trace it in vector. No need to do it by hand! You can do this simply by clicking on the inserted picture and using the window Path> Trace Bitmap window. You'll see a lot of tracing options, so do several tests until you find the one that's right for you. Make sure your traced shapes are presented in a uniform, flat color.

Now close the 'Trace Bitmap' window. The original image remains behind the tracing, so select it and delete it.
Then, click on the traced image with the tool 'Edit paths by nodes'. If the tracing worked correctly, you should be able to see the vectors all around the individual parts of the traced image.
Finally, to choose the desired raster input level, select all the traced elements and set the fill color using the window Object> Fill and Stroke.
How to remove double lines
If you place two objects next to each other, in such a way as to match the ends, it is very likely that you get the overlap of the cutting lines.
Double lines are quite easy to spot at a glance, as they are presented in a darker blue than other cutting lines. It is necessary to eliminate these double lines in order to obtain a single cutting line, or, for better say, a shared cutting line; otherwise the laser will literally cut the same part twice (which is not ideal either for the performance on the material, or for your estimate!).
Here is the procedure to remove the double lines:
Step 1: Select one of the two adjacent objects and use the command Path> Object to Path.
Step 2: Select the 'Edit paths by nodes' tool:

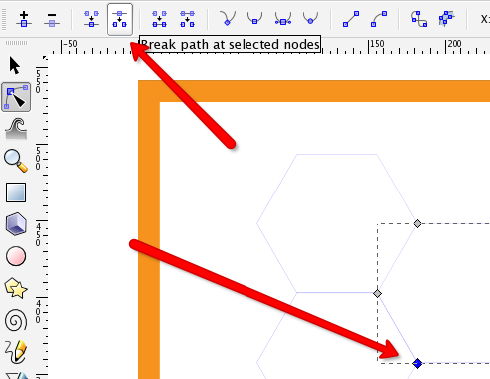
Step 3: Click on an object that contains a double line, then select a node at the end of the line you want to remove:

Step 4: With the node highlighted in dark gray, click the 'Break path at selected nodes' button:

Step 5: Click on the node at the other end of the double line and use the 'Break path at selected nodes' button again:

Step 6: Click on the line between the two nodes so that both are highlighted in dark gray (and become larger than the other nodes of the object) and press delete (backspace) on the keyboard. There is a lighter blue line compared to the previous one.

Step 7: Select the nodes at each end of the following line and repeat the procedure:
Export the file
Use the command File> Save as and select the 'Inkscape SVG' format:

Done! Now you can upload the file
or read the FAQ
or even look at our video tutorial In English made for the Jobs of the Future project

